Hormonal Replacement Therapy (HRT) is a medical treatment that helps manage symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances, particularly during menopause, but it can also be used for other hormonal deficiencies. As women age, particularly around the time of menopause, estrogen and progesterone levels decline, leading to various physical and emotional symptoms. HRT aims to alleviate these symptoms and improve quality of life. There are several types of Hormonal Replacement Therapy in Dubai, each with unique characteristics and uses. This article explores the different types of HRT available, their applications, benefits, and potential risks.
1. Estrogen Therapy
Estrogen therapy is one of the most common forms of HRT and is primarily used to treat menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. Estrogen can be administered in several ways:
Oral Tablets: Estrogen is taken in pill form. This method is convenient but may have varying absorption rates in different individuals.
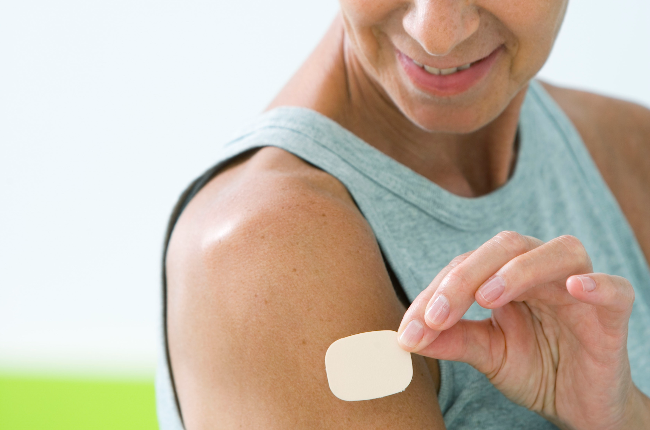
Transdermal Patches: These are adhesive patches that release estrogen through the skin into the bloodstream. They can provide a steady dose and minimize liver metabolism.
Gels and Creams: Topical applications allow estrogen to be absorbed directly through the skin. They can be applied to specific areas, offering localized treatment for symptoms such as vaginal dryness.
Vaginal Rings: These are flexible rings inserted into the vagina that release estrogen directly to the vaginal tissues, providing relief from dryness and discomfort.
2. Combined Hormone Therapy
Combined hormone therapy involves the use of both estrogen and progestin (a synthetic form of progesterone). This type of therapy is typically recommended for women who have not had a hysterectomy because estrogen alone can increase the risk of endometrial cancer. The combination helps protect the uterine lining. Like estrogen therapy, combined therapy can be administered in various forms:
Oral Tablets: These pills usually contain both hormones in a single or sequential regimen.
Transdermal Patches: Patches that deliver both hormones are available, providing a convenient and effective method.
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs): Some IUDs release progestin directly into the uterus, which can help control heavy bleeding while providing localized hormone treatment.
3. Bioidentical Hormone Replacement Therapy (BHRT)
Bioidentical hormones are chemically identical to the hormones produced by the human body. BHRT is often marketed as a more natural alternative to traditional HRT, and it can be customized to match an individual’s specific hormonal needs. BHRT can be delivered through:
Custom Compounded Creams and Gels: These are tailored formulations prepared by specialized pharmacies based on an individual's hormone levels.
Pellets: Small pellets containing bioidentical hormones can be implanted under the skin, providing a slow, continuous release of hormones over several months.
Oral Tablets: BHRT can also be taken in pill form, although the custom compounded option is often preferred for its personalization.
4. Testosterone Therapy
While testosterone is often associated with male health, it plays an important role in women’s health as well. Low testosterone levels can lead to fatigue, decreased libido, and mood changes. Testosterone therapy is less common than estrogen therapy but is gaining recognition. It can be administered through:
Injections: Testosterone can be injected into the muscle, providing an effective boost to testosterone levels.
Patches: Transdermal patches for testosterone are available, allowing for steady absorption.
Topical Gels: Similar to estrogen gels, these allow for direct absorption through the skin.
5. Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs)
SERMs are a class of drugs that selectively modulate estrogen receptors in different tissues. They can act as estrogen agonists in some tissues and antagonists in others. While they are not traditional HRT, they can be used to treat specific symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances, particularly in women with breast cancer. Examples include:
Raloxifene: Used primarily to prevent osteoporosis in postmenopausal women, it mimics estrogen's protective effects on bones without stimulating breast tissue.
Toremifene: This is used in the treatment of breast cancer and can also have a positive impact on bone density.
6. Hormonal Contraceptives
While primarily used for birth control, hormonal contraceptives can also provide relief from menopausal symptoms. Combined oral contraceptives, hormonal IUDs, and contraceptive implants can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce hot flashes in perimenopausal women.
Benefits of HRT
HRT can significantly improve quality of life by alleviating menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and vaginal dryness. It can also help prevent osteoporosis and reduce the risk of heart disease when started early. Many women report improved energy levels, better sleep quality, and enhanced sexual function.
Risks and Considerations
While HRT can be beneficial, it is not without risks. Potential side effects may include weight gain, breast tenderness, and an increased risk of blood clots, stroke, and certain cancers, particularly when using estrogen alone. It's essential for individuals considering HRT to discuss their medical history and risk factors with their healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Conclusion
Hormonal Replacement Therapy offers a range of options for managing symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances, particularly during menopause. Understanding the different types of HRT—estrogen therapy, combined therapy, bioidentical hormones, testosterone therapy, SERMs, and hormonal contraceptives—allows women to make informed decisions about their health. While HRT can provide significant benefits, it is essential to weigh these against potential risks and work closely with a healthcare provider to create a tailored approach that suits individual needs and preferences.
