
One of the most common concerns of hair loss victims is what treatments are available to prevent hair loss. Your hair may be falling out for various causes; therefore, determining the cause can be challenging. There are ways you can evaluate whether this is temporary, curable, or permanent. Before identifying the reason, your dermatologists will most likely perform a physical check on you and inquire about your diet, lifestyle, hair care routine, and family’s medical history. “Will the hair grow back?” is the only question many individuals have after diagnosing the cause of hair loss. Alopecia is the medical term for hair loss. Alopecia isn’t only a human problem; you’ve probably seen those ripped chimps with Alopecia.
This review will cover the most common hair loss diagnosis methods and why consulting Dermatologists is essential in determining causes of hair fall disease. In a recent post, we discussed the shocking truth about female hair loss and the causes of female hair loss.
Diagnosing Hair Loss
Dermatologists employ several tests to diagnose the causes of hair loss or premature hair loss. Let’s take a look at how dermatologists determine the cause of your hair loss before moving on to possible treatments. The reason for your baldness or hair loss can be a genetic issue, medical condition, or environmental. If you notice that you are getting bald or losing hair, the first thing you must do is consult a doctor to get a diagnosis rather than making assumptions at home. Note that all of the diagnostic tests described below can be performed at your Dermatologist’s clinic, which is why it’s important to consult a doctor so you can get everything done under one roof.

1. Medical & Family History
Your doctor may ask several questions to learn more about your medical and family history. Basically, your Dermatologist needs to know when your hair loss began, your diet, your hair care routine, whether you’ve lately given birth, whether you suffer from stress or anxiety, your occupation, whether hair loss runs in your family, your symptoms, and any other medical conditions you have. Even if some questions appear to be unrelated, make sure to provide accurate information.
Physical Exam
Your Dermatologist will carefully examine your hair to discover if there are any sores, redness, inflammation, or scarring on your scalp. Medical health screening for hair loss may include Blood Tests [Complete Blood Count (CBC), Thyroid Function Test (TFT)], Pull Test, Scalp Biopsy, Fungal Culture, Trichromatic Analysis.
2. Blood Test
If a blood test confirms that you are deficient in Biotin, Iron, or Zinc, your Dermatologist may advise you to take a supplement. If you aren’t taking enough protein, your Dermatologist can advise you on how to increase your protein intake. It would be best not to take Biotin, Iron, or Zinc unless you have a prescription. When your vitamin and mineral levels are normal or adequate, taking a supplement can be detrimental. Other supplements on the market meant to aid with hair loss often contain a high concentration of specific nutrients. This can result in an excessive amount of nutrients, so many dermatologists prescribe taking a multivitamin instead.
For example, People may experience nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and headaches if they too much Zinc. If they continued to consume too much Zinc for an extended period, they might also experience issues such as low copper levels, low immunity, and low HDL Cholesterol (Also known as Good Cholesterol)
Women with thin hair but no bald spots may be suffering from a hormonal imbalance induced by high levels of Androgens. It is a hormone class that contains testosterone. Hair loss and baldness, facial hair, hair growth on the chest or abdomen, menstrual irregularities, and acne are all symptoms of androgen excess. An increased androgen level can be detected with a blood test.
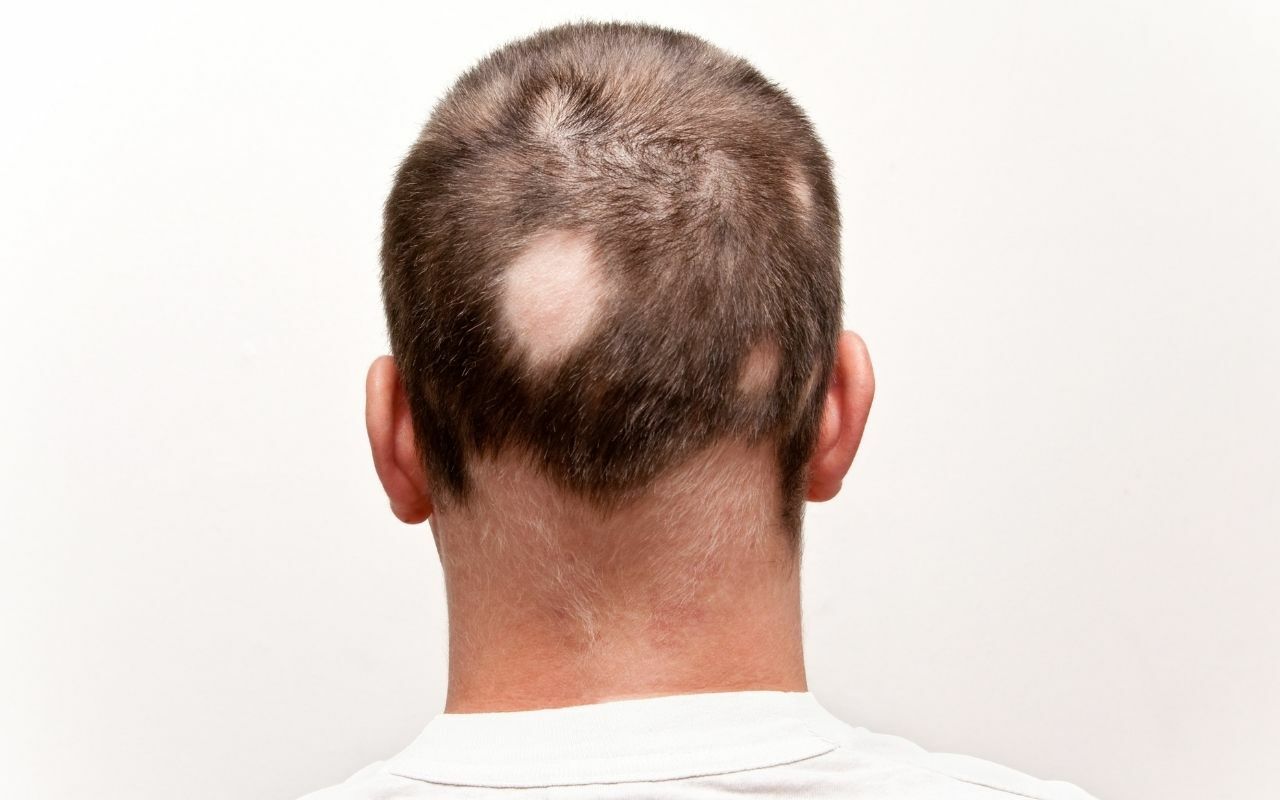
3. Hair Pull Test
This is a simple test used to detect active hair loss and should be performed on every patient complaining of hair loss. A dermatologist does a pull test by gently tugging on small sections of hair (approximately 40 to 50 strands) from different parts of the scalp. The easy extraction of more than six hair fibers indicates that you suffer from one of the following hair fall diseases.
Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a form of temporary hair loss disorder that occurs after a stressful, shocking, or traumatic incident. It is most commonly found on the top of the scalp. You may notice a significant volume of hair fall out, but it will grow back.
Anagen Effluvium
Anagen effluvium, also known as chemotherapy-induced Alopecia, is a form of non-scarring Alopecia that is usually associated with chemotherapy. Affected anagen hairs are subjected to a toxic or inflammatory insult, resulting in hair shaft fracture.
Loose Anagen Syndrome
Loose Anagen Hair (LAH), also known as the Loose Anagen Syndrome (LAS), is a condition characterized by defective anagen hair anchoring. It is most commonly reported in childhood (predominantly in young girls aged between 2 to 6 years), though it can occur at any age.
Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic Alopecia, also known as Male Pattern Baldness or Female Pattern Baldness, is the most common type of hair loss condition. The initial signs of baldness include a receding hairline, thinning hair throughout the entire scalp and a balding crown. However, Women’s genetic hair loss is a little different from men’s. Women’s hair thins all over the head, but the hairline does not recede.

4. Scalp Biopsy
Numerous small samples of skin were removed from an affected area of the scalp to support a clinical examination. The excised tissue is submitted to a laboratory to be examined by a pathologist specializing in scalp conditions. First, a local anesthetic is administered into the area to sedate the affected skin before the Dermatologist taking the sample skin for clinical evaluation. Next, a few stitches or cauterization with an electrical current are used to seal the wound.
5. Fungal Culture
Tinea Capitis is a scalp fungal infection that affects both the skin and the hair. Ringworm of the scalp is another name for it. Hair loss, dry scaly spots, redness, and itching are all symptoms of tinea capitis.
Tinea Barbae is a similar condition that affects the beard area. Fungal culture enables the identification of the underlying cause for fungal infection. A dermatologist may scrape or swab the scalp to collect a small portion of skin or hair for testing in a laboratory. It is, however, extremely slow, requiring up to four weeks, and immediate attention or treatment is required before the result is known.
6. Trichometry
Trichometric Analysis can help you obtain pertinent data regarding hair loss, such as overall average rates of hair density, thickness, growth, and shedding for a given patient based on diagnostic data. It also enables the comparison of data obtained through Trichometric Analisis to scientifically established standards for a healthy person, differentiated by sex, age, and clinical, biological, genetic, or epigenetic factors (Racial Differences) associated with hair loss.
7. Clinical Photography Of The Hair
Dermatologists employ digital photography to document the hair loss condition or to evaluate progress/response to treatments. During your first visit, your Dermatologists may take photos from various angles and compare them to pictures captured during subsequent sessions to assess progress. Taking Photos of Hair Loss for Online Diagnosis is becoming increasingly common these days, owing to travel restrictions in some countries severely affected by the Covid 19 pandemic.
The cause of your hair loss might be an underlying health issue, which is why it is essential to consult a Dermatologist so that the causative agent for possible hair fall disease can be precisely determined. It is not advisable to make assumptions and go for home remedies. One of the reasons the condition worsens is failing to diagnose the causes of hair loss.
In addition, not giving the required attention to your hair loss may lead to depression, anxiety, and social phobia. Depression can cause sleep deprivation, depressed mood, a lack of interest or pleasure in activities, and fatigue. Anxiety can lead to excessive concern and trouble managing one’s emotions. You will be conscious of your own heartbeat, which is uncomfortable. Feel as though your heart has skipped or stopped beating. Sweating may also irritate you. Social anxiety disorder, often known as social phobia, is a mental disorder. It is a constant and deep fear of humiliation or being judged negatively by others. Do not let hair loss fall apart your whole life. Instead, consult a Dermatologist and get the necessary treatment promptly.
