Structure (3-3-3-3-3) OR (5-3-5-3-5)
In real-time charting, you should NEVER label a developing wave as a leading diagonal. These are so rare you should not even consider them as an option. You should label leading diagonals as such only on past charts when there is no other wave count that fits.
A beginning wave pattern. May only form as Wave 1 or as Wave A of a Zigzag. .
Elliott Wave International notes that the vast majority of leading diagonals divide into 3 wave substructures (3-3-3-3-3), but also note that a few have been found with 5-3-5-3-5 structure, yet Wave 4 will still enter the price territory of Wave 1 - which is what makes it a diagonal.
It would also be safe to say that, since W4 can overlap W1 in a leading diagonal, there may be situations where a 1-2 1-2 count isn't working out because it was a mislabeled leading diagonal rather than a 1-2 1-2. Best to keep this in mind in when exploring alternate wave counts when a 1-2, 1-2 count isn't working out.
As with ending diagonals, this wave develops more as a diagonal wave than a typical fast moving impulse wave.
It is a Motive Wave, therefore shares some of the same characteristics as an impulse wave. W2 may never cross the origin of W1 and W3 may never be the shortest wave. However, unlike impulse waves, W4 will (almost) always cross into the W1 territory. This "almost" leaves open the possibility that Wave 1 could be a 3-3-3-3-3 structure without wave 4 overlapping wave one. Curious indeed.
Frequently you will see a throw-over the trend line in wave 5. You can almost expect to see it. Very normal attempt to shake out weak hands before moving in the opposite direction.
Notes:
Diagonals are usually followed by a quick thrust in the direction of the next wave that completely eclipses the diagonal wave. That normally completes takes only 1/2 to 1/3 of the time it took for the pattern to form.
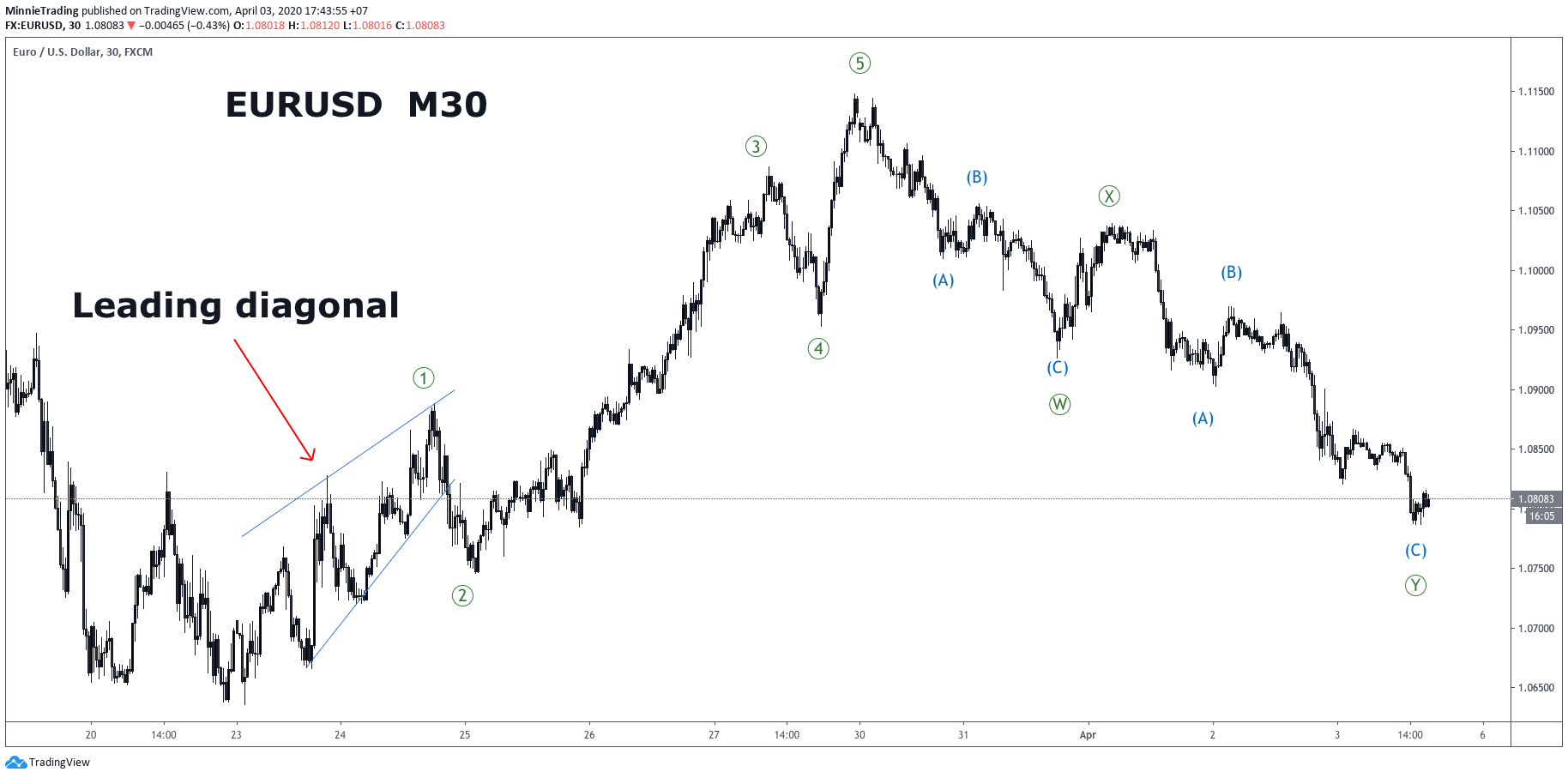
Sample Leading diagonals in wave 1
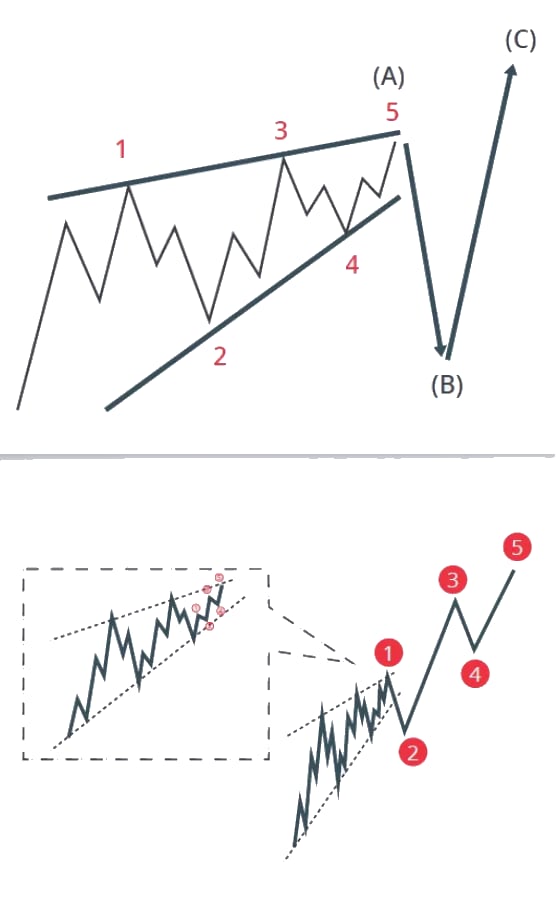
Leading diagonals in wave A and wave 1
CONTENT OF ELLIOTT WAVE CHEAT SHEETS
1 Home Rules and Guidelines Applicable to All Motive and Corrective Waves
2 Wave 1 Characteristics and Structure
3 Wave 2 Characteristics and Structure
4 Wave 3 Characteristics and Structure
5 Wave 4 Characteristics and Structure
6 Wave 5 Characteristics and Structure
7 Wave A Characteristics and Structure
8 Wave B Characteristics and Structure
9 Wave C Characteristics and Structure
10 Extensions Structure and Trading
11 Fibonacci Targets Price Targets for Retracement and Extension
12 1-2/1-2 Structures Wave 1-2 /1-2 Characteristics
13 Zigzags Structure and characteristics
14 Flats This is All FLAT Rules
15 Triangles Triangles (3-3-3-3-3) Description and samples
16 Complex Corrections Characteristics of Complex Corrections (Combinations)
17 Declaring X Waves When to declare an X wave and a complex correction
18 Ending Diagonals Description and samples.
19 Leading Diagonals Description and samples. This is quite rare.
21 Channeling How to Use Channels to Identify Waves
22 Correction Times Use the appropriate time frame to analyze the correction.
