Introduction
In this guide, we will delve into the intricacies of preparing for palate repair surgery, also known as palatoplasty. Palate repair surgery is a crucial procedure for individuals born with a cleft palate, a congenital condition that affects the roof of the mouth. By understanding the preparation process thoroughly, patients can ensure a smoother surgical experience and optimize their recovery.
Understanding Palate Repair Surgery
Palate repair surgery aims to correct a cleft palate, a birth defect where the roof of the mouth has a split or opening. This condition can lead to difficulties in feeding, speech development, and ear infections. Palatoplasty is typically performed in infancy or early childhood but can also be done in adulthood if necessary.
Importance of Preparation
Preparation is key to ensuring the success of any surgical procedure.Palate Repair Surgery in Dubai, adequate preparation can minimize risks, enhance recovery, and optimize outcomes. This involves physical and emotional readiness, as well as logistical arrangements.
Types and Categories
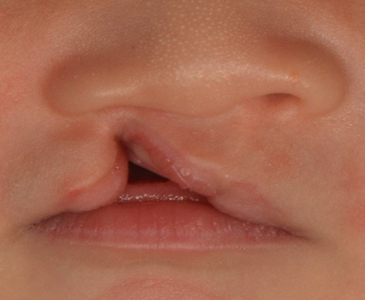
Types of Cleft Palate
Complete Cleft Palate: In this type, the cleft extends through the entire palate, from the front of the mouth to the back.
Incomplete Cleft Palate: Here, the cleft does not extend entirely through the palate, leaving some tissue intact.
Categories Based on Severity
Unilateral Cleft: A cleft occurring on one side of the palate.
Bilateral Cleft: Clefts present on both sides of the palate.
Symptoms and Signs
Common Symptoms
Visible Split in the Roof of the Mouth: The most apparent sign of a cleft palate.
Feeding Difficulties: Infants may have trouble sucking or swallowing milk.
Speech Problems: Difficulty in pronouncing certain sounds due to the opening in the palate.
Uncommon Symptoms
Ear Infections: Fluid buildup in the middle ear due to improper drainage.
Dental Issues: Misalignment of teeth and jaw due to the cleft.
Causes and Risk Factors
Biological Factors
Genetic Factors: Cleft palate can be hereditary, with certain genetic mutations increasing the risk.
Fetal Development: Abnormalities during fetal development can lead to a cleft palate.
Environmental Factors
Maternal Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, alcohol consumption, and certain medications during pregnancy can increase the risk.
Exposure to Toxins: Environmental factors such as pollution or chemical exposure may contribute.
Lifestyle Factors
Poor Nutrition: Maternal malnutrition during pregnancy can affect fetal development.
Lack of Prenatal Care: Inadequate prenatal care may lead to undetected issues.
Diagnosis and Tests
Prenatal Diagnosis
Ultrasound: Can sometimes detect a cleft palate during routine prenatal ultrasounds.
Amniocentesis: Genetic testing may identify certain abnormalities associated with cleft palate.
Postnatal Diagnosis
Physical Examination: A visual inspection of the baby's mouth after birth.
Imaging Tests: X-rays or CT scans may be performed to assess the extent of the cleft.
Treatment Options
Surgical Repair
Palatoplasty: The primary surgical procedure to repair a cleft palate.
Timing: Surgery is typically performed between 6 and 18 months of age, but timing may vary depending on individual circumstances.
Therapies
Speech Therapy: Helps improve speech development and articulation.
Feeding Intervention: Techniques to assist infants with feeding difficulties.
Preventive Measures
Prenatal Care
Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintain a balanced diet, avoid smoking and alcohol, and attend regular prenatal check-ups.
Genetic Counseling: For families with a history of cleft palate surgery, genetic counseling can provide valuable information and support.
Postnatal Care
Follow-Up Visits: Regular follow-up appointments with pediatricians and specialists to monitor development.
Early Intervention Programs: Enrollment in early intervention programs can provide support for speech and language development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, preparing for palate repair surgery involves understanding the condition, addressing its symptoms, identifying risk factors, and exploring treatment options. By following preventive measures, seeking timely diagnosis, and accessing appropriate care, individuals with cleft palate can achieve improved outcomes and lead fulfilling lives.
