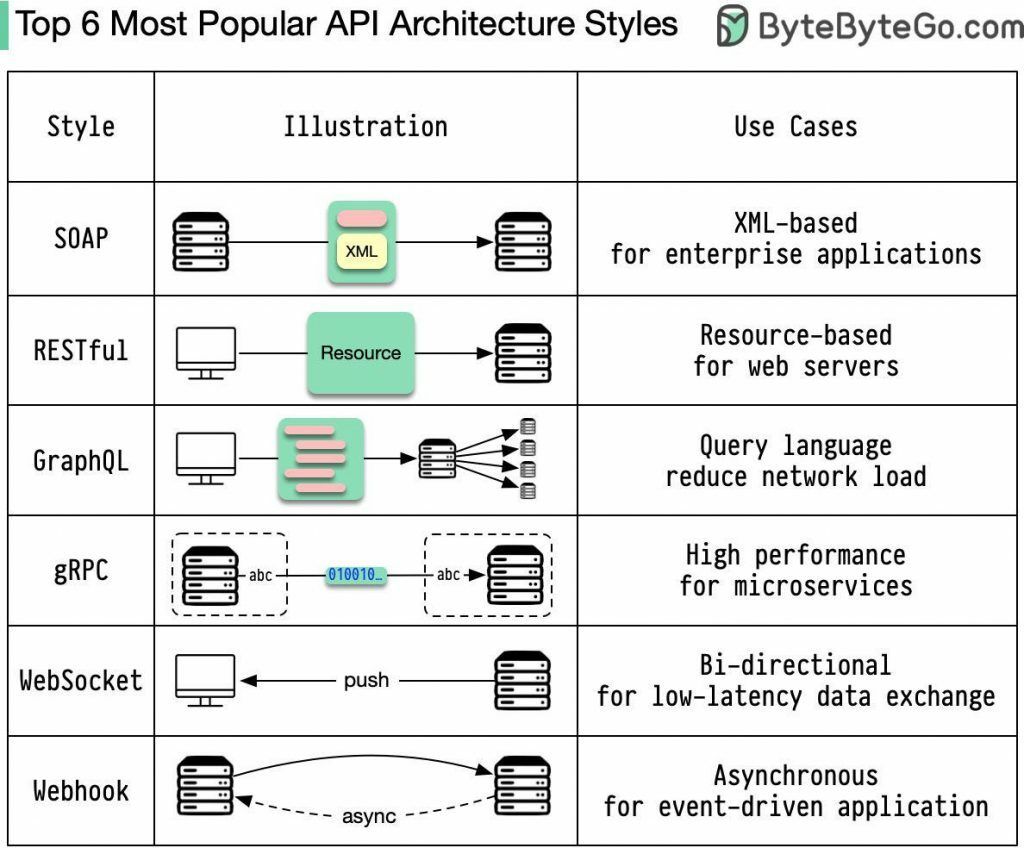
Some common API architecture styles include:
REST (Representational State Transfer):
Principles: REST is based on a set of architectural principles, including statelessness, client-server architecture, and a uniform interface.
Communication: RESTful APIs use standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) for communication and rely on the stateless nature of HTTP.
Data Format: Typically, REST APIs use standard data formats such as JSON or XML for data representation.
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol):
Protocol: SOAP is a protocol for exchanging structured information in web services.
Communication: It relies on XML as the message format and can use various protocols for communication, including HTTP and SMTP.
Complexity: SOAP APIs tend to be more complex compared to REST, as they have a rigid specification and require more overhead.
GraphQL:
Query Language: GraphQL is a query language for APIs that allows clients to request only the data they need.
Flexibility: Unlike REST, where the server defines the structure of the response, GraphQL lets clients specify the structure of the response.
Single Endpoint: GraphQL typically exposes a single endpoint for all operations.
RPC (Remote Procedure Call):
Procedure Calls: RPC allows a program to cause a procedure (subroutine) to execute in another address space (commonly on another machine).
Communication: It can use various protocols for communication, including HTTP, JSON-RPC, and XML-RPC.
Tight Coupling: RPC can result in tight coupling between the client and server.
WebSocket:
Real-time Communication: WebSocket enables full-duplex communication between a client and a server, allowing real-time updates.
Low Latency: It is suitable for applications requiring low-latency communication, such as chat applications and real-time collaboration tools.
gRPC (gRPC Remote Procedure Calls):
Protocol Buffers: gRPC uses Protocol Buffers (protobuf) as the interface definition language and supports multiple programming languages.
Efficiency: It is known for its efficiency, supporting features like bidirectional streaming and multiplexing.
These architecture styles serve different purposes and have trade-offs, so the choice of which one to use depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the application or system being developed.
