Structure
Triangles only form in Waves 4, B, and X, the waves prior to the terminating wave of the structure.
There are five Waves (A-E) and each wave will normally subdivide into a 3 wave structure such as a Zagzag.
A running triangle is said to have formed when the B wave exceeds the origin of WA. (think expanded flat.)
There are three types of triangles. The most common are the contracting, symmetrical kind. Barrier triangles form where one side resembles a horizontal line, and expanding triangles, which are very rare.
Wave C, or occasionally wave D, will normally become complex and form a double (WXY) or triple Zigzag (WXYXZ) formation. X can be a triangle itself.
Infrequently, Wave E can develop into a smaller triangle, making a total wave count of 9 waves, labeled A-E, with the interior triangle labeled a-e of the next lesser degree. The ending pivot is E e.
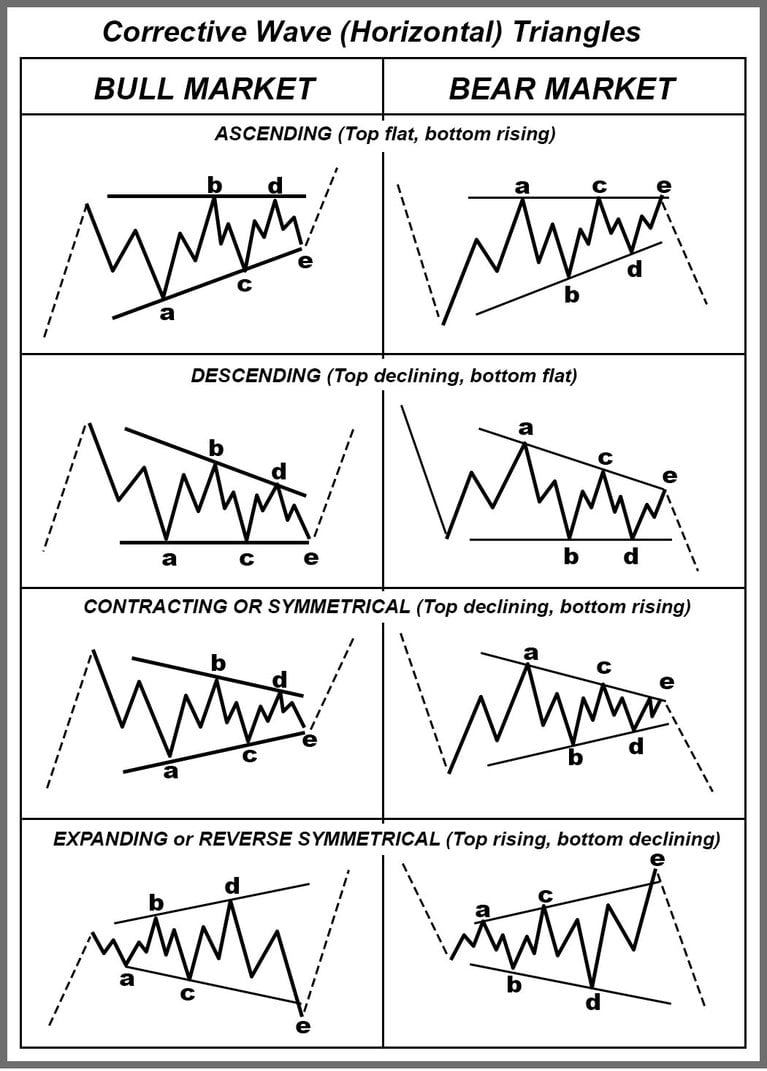
EXPANDING (REVERSE SYMMETRICAL ) TRIANGLE SAMPLE

Specifics
In a wave 2, a triangle may only form in wave B of the retracement. It can not comprise the entire wave 2. However, in wave 4, a triangle may form as the entire wave 4 structure or as wave B in the wave structure. These will resolve in opposite directions, so you need to be right on where the triangle is located.

Retracement
Triangles rarely follow retracement rules, but these are the stated retracements
Contracting and Symmetrical Triangles
In a triangle, at least two waves frequently have a .618 relationship with their prior wave.
With a running triangle you can expect Wave B to reach 1.382 of Wave A, before the remainder of the triangle falls into suit with .786 retracements. The relationships are somewhat more expanded than regular triangle relationships.
Expanding Triangles
As a general rules, these triangles conform to 1.618 relationships between the waves.
CONTENT OF ELLIOTT WAVE CHEAT SHEETS
1 Home Rules and Guidelines Applicable to All Motive and Corrective Waves
2 Wave 1 Characteristics and Structure
3 Wave 2 Characteristics and Structure
4 Wave 3 Characteristics and Structure
5 Wave 4 Characteristics and Structure
6 Wave 5 Characteristics and Structure
7 Wave A Characteristics and Structure
8 Wave B Characteristics and Structure
9 Wave C Characteristics and Structure
10 Extensions Structure and Trading
11 Fibonacci Targets Price Targets for Retracement and Extension
12 1-2/1-2 Structures Wave 1-2 /1-2 Characteristics
13 Zigzags Structure and characteristics
14 Flats This is All FLAT Rules
15 Triangles Triangles (3-3-3-3-3) Description and samples
16 Complex Corrections Characteristics of Complex Corrections (Combinations)
17 Declaring X Waves When to declare an X wave and a complex correction
18 Ending Diagonals Description and samples.
19 Leading Diagonals Description and samples. This is quite rare.
21 Channeling How to Use Channels to Identify Waves
22 Correction Times Use the appropriate time frame to analyze the correction.
